This guide will demystify these key concepts by breaking down how they work and why the distinctions matter for your bottom line.
1. The Two Types of Hosting: Where Your Website Lives
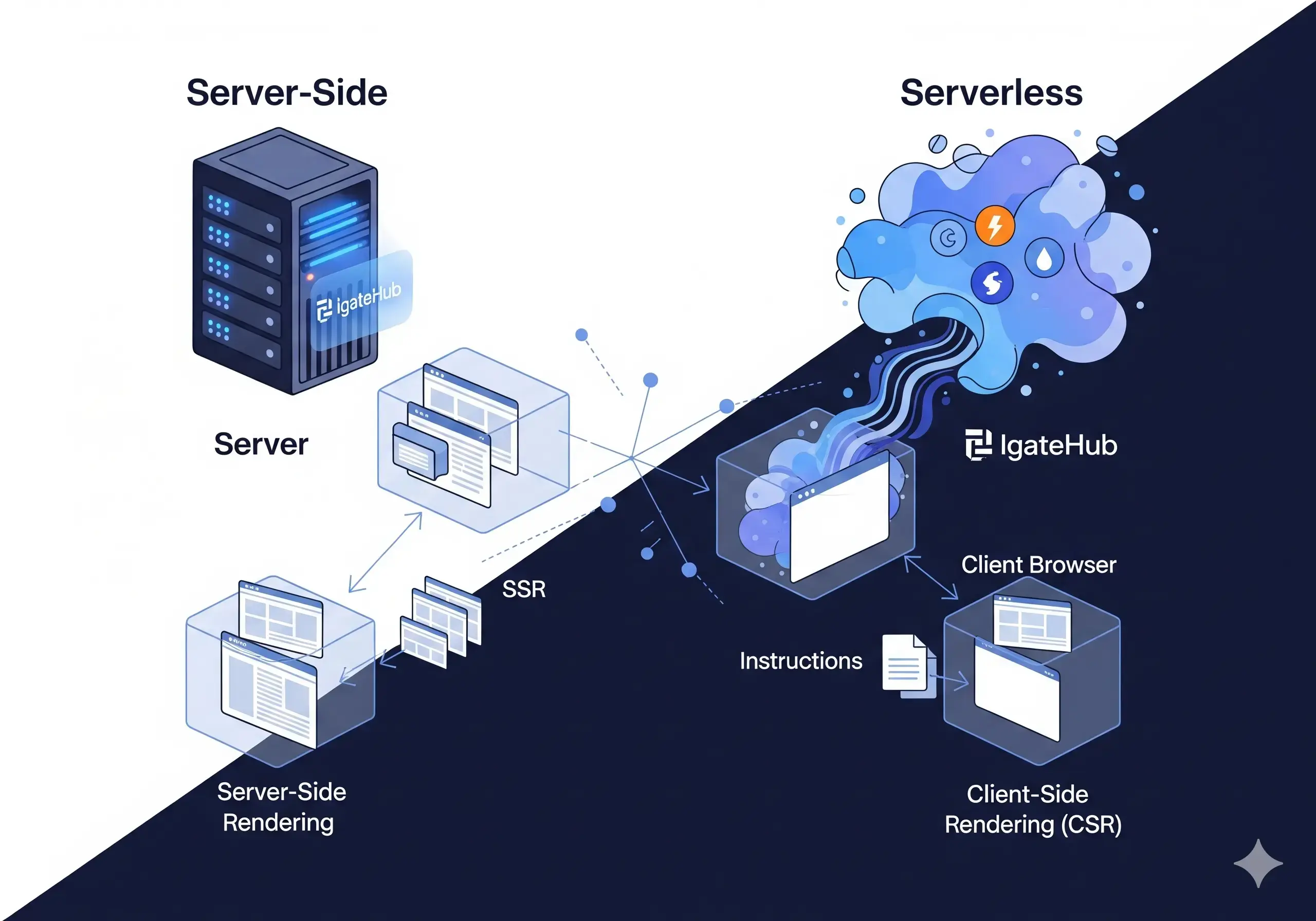
This is about where your website’s core files and code are stored and run. It’s the difference between owning an office and using a taxi service.
Server-Side Hosting (The Traditional Office)
- What it is: With traditional server-side hosting, you rent or own a dedicated computer (server) that is online 24/7. This server is always running, waiting for visitors to your website. You have full control over this environment, but you are also responsible for its upkeep.
- Analogy: Think of this as renting a dedicated office space. You pay a fixed monthly rent for the entire space, whether you have 100 clients visiting every day or no one at all. You're in charge of all the maintenance, from electricity to security.
- Pros: Total control, great for highly customized or complex applications that need constant resources.
- Cons: Can be expensive and inefficient for low-traffic sites. You have to handle all maintenance and scaling manually.
Serverless Hosting (The On-Demand Taxi Service)
- What it is: With serverless, you don't rent a constant server. Instead, your code is stored on a cloud platform and only runs for the exact moment it's needed (e.g., when a visitor clicks a button). The server is managed entirely by the cloud provider. You just provide the code.
- Analogy: This is like using a taxi service. You don't own a car; you just pay for the ride when you need it. When the ride is over, the car goes away. You pay only for the moments your code is running, and the service handles all the scaling and maintenance for you.
- Pros: Highly cost-effective (you only pay for what you use), scales automatically to handle sudden traffic spikes, and requires no server maintenance from you.
- Cons: Less control over the server environment, which might not be suitable for all types of applications.
2. The Two Types of Rendering: How Your Website is Built
This is about when and where a webpage's content is assembled. Is it built on the server and sent to the user, or is it built inside the user's web browser?
Server-Side Rendering (SSR) (The Pre-Built LEGO Set)
- What it is: The server does all the work of building the webpage. When a user requests a page, the server fetches all the data, assembles the complete HTML file with all the content, and then sends this finished product to the user's browser. The browser's job is simply to display it.
- How it works: This is the traditional way websites have been built for decades, and it's how frameworks like Laravel and basic HTML/CSS/JavaScript sites work.
- Pros: Extremely fast initial page load because the user gets a complete page right away. Excellent for SEO, as search engines can easily "read" all the content from the HTML.
- Cons: Every page view often requires a full page refresh, which can feel less fluid. The server has to work harder to build each page for every request.
Client-Side Rendering (CSR) (The Box of LEGOs and Instructions)
- What it is: The user's web browser does the work. The server sends a very small, basic HTML file that contains a link to a large JavaScript file. The browser downloads the JavaScript and then builds the entire webpage right there on the user's device.
- How it works: This is the method used by modern Single-Page Applications (SPAs) built with frameworks like React.js and Vue.js.
- Pros: Navigation between pages is incredibly fast and fluid after the initial load, because the browser doesn't have to reload the entire page. It feels more like a desktop application.
- Cons: The initial page load can be slow, especially on slower devices, as the browser has to download and run a lot of JavaScript before anything is visible. Can be challenging for SEO, as search engines might struggle to index content that is built by JavaScript.
Hybrid Rendering (The Best of Both Worlds)
Modern frameworks like Next.js (for React) and Nuxt.js (for Vue.js) offer a solution that combines both SSR and CSR. They allow you to choose which pages are pre-built on the server (for SEO and fast initial loads) and which are built on the client (for a highly interactive experience). This gives you the best performance and SEO balance for your entire website.
3. Making the Right Choice for Your Business
So which combination is best for you?
- For Blogs, E-commerce, or Content-Heavy Websites: You need great SEO and fast initial loads. Server-Side Rendering (SSR) is an excellent choice, and Laravel is a powerful framework for this.
- For User Dashboards, Analytics, or Highly Interactive Web Apps: The initial load time is less important than the fluid, app-like experience. Client-Side Rendering (CSR) or a hybrid approach with Next.js or Nuxt.js would be ideal.
- For Infrastructure: If you have unpredictable traffic and want to save money on hosting and maintenance, Serverless Hosting is a strong option. If you need total control and constant resources for a complex system, Server-Side Hosting is the way to go.
At IgateHub, we understand these complexities and help you choose the right combination of technologies to ensure your project is not only built beautifully but is also optimized for your business goals, performance, and budget.